Gout Treatment Specialist in Glen Burnie MD
Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis triggered by the crystallization of excess uric acid in the joints, leading to sharp pain, swelling, and redness, often in the big toe. Treatment focuses on medications to lower uric acid, dietary adjustments, and lifestyle changes to prevent further attacks. Dr. Nasser Nasseri, MD, and our dedicated team will help you with comprehensive Gout treatment. For more information, contact us or request an appointment online. We are located at 203 Hospital Dr, Suite 300B, Glen Burnie, MD 21061.


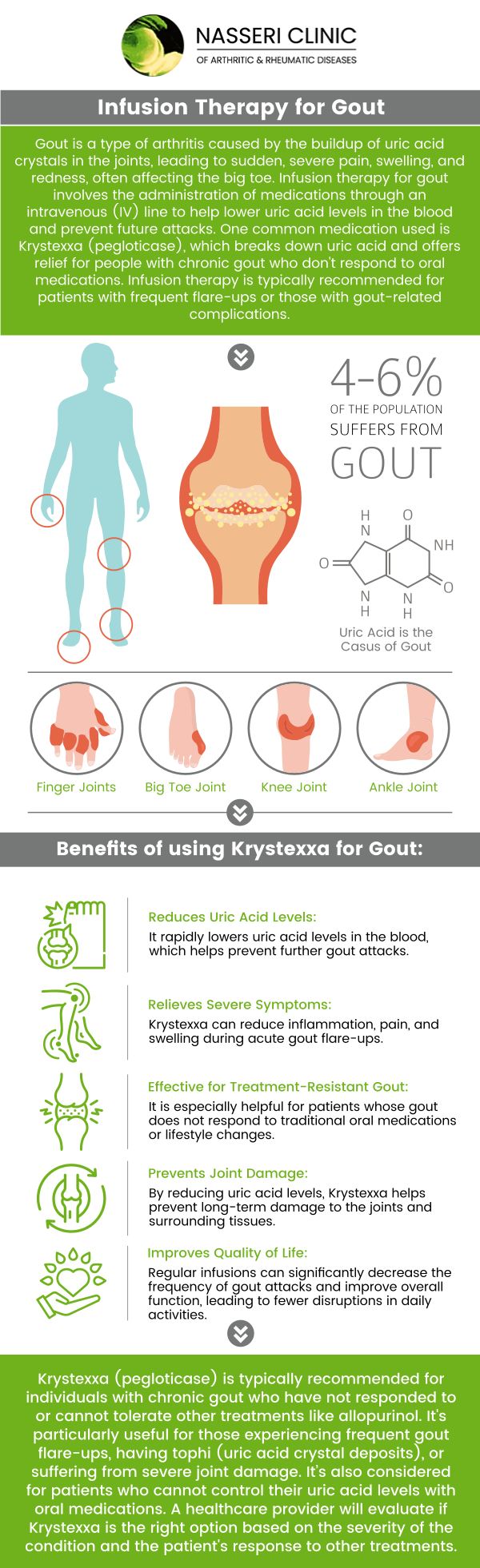
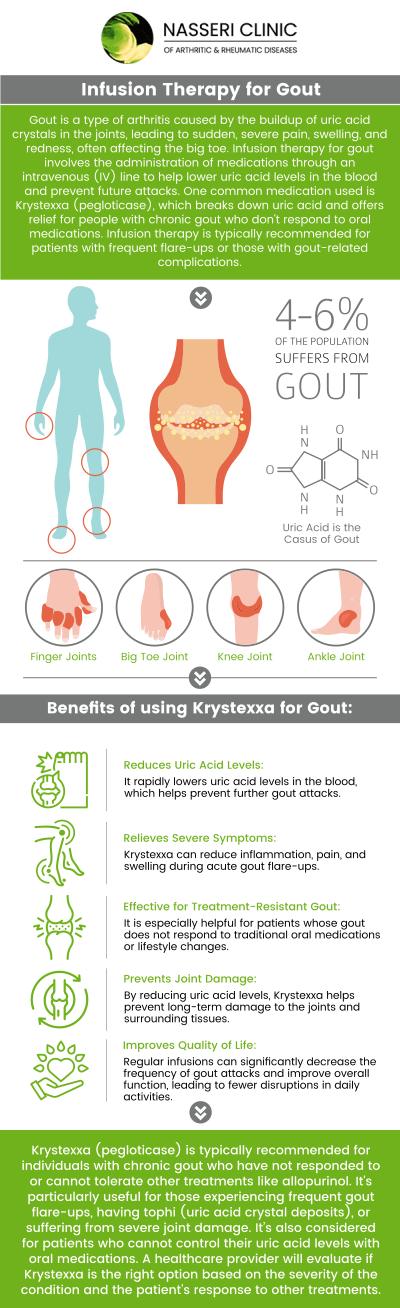
Table of Contents:
What is gout?
What are gout symptoms?
What causes gout?
What tests will be done to diagnose gout?
Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis characterized by sudden, severe attacks of pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness in the joints. It most commonly affects the joint at the base of the big toe but can also occur in other joints such as the ankles, knees, elbows, wrists, and fingers.
Gout is caused by an excess of uric acid in the blood, which is referred to as hyperuricemia. Uric acid is produced when the body breaks down purines, which are substances found in certain foods and drinks such as red meat, seafood, alcohol, and sugary beverages. When uric acid levels are too high, it leads to the formation of sharp, needle-like crystals in the joints, resulting in the intense pain and inflammation characteristic of gout.
Frequently observed symptoms of gout include:
• Intense joint pain – Gout is characterized by severe pain in one or more joints. The pain often starts at night and can be excruciating.
• Swelling and redness – You may notice the affected joint becoming puffy, red, or hot to the touch. This occurs due to uric acid crystals accumulating in the joint, leading to inflammation and swelling.
• Tenderness – Even a light touch or pressure on the affected joint can be extremely painful. The tenderness can make it difficult to wear shoes or perform daily activities.
• Limited range of motion – As the gout attack progresses, the affected joint may become stiffer and less flexible. This can hinder movement and make it challenging to perform regular activities.
• Tophi – In some cases, urate crystals can form lumps under the skin called tophi. These lumps are typically not painful at first but can become inflamed and tender during a gout flare-up.
Another characteristic symptom of gout is lingering discomfort. After severe pain subsides, milder joint discomfort may last for days or weeks.
The cause of gout is an excess of uric acid in the blood, or hyperuricemia. Several factors can contribute to the development of hyperuricemia, such as:
• Diet – If you consume foods and drinks high in purines often, such as red meat, seafood, alcohol, and sugary beverages, you are more likely to develop gout.
• Medical conditions – Certain health conditions increase the risk of gout, such as obesity, high blood pressure, diabetes, and kidney disease.
• Medications – Diuretics, low-dose aspirin, and certain drugs used to manage hypertension can raise uric acid levels and increase the risk of gout.
• Age and gender – Men are more likely to develop gout than women, particularly between the ages of 30 and 50. Postmenopausal women are also at elevated risk of gout due to changes in estrogen levels.
• Genetics – A family history of gout increases the likelihood of developing the condition, suggesting a genetic predisposition.
Some of the diagnostic tests that healthcare professionals often perform to confirm a gout diagnosis include:
• Joint fluid analysis – The most definitive test for gout is joint fluid analysis. A needle is used by a healthcare provider to extract fluid from the affected joint in a procedure known as arthrocentesis. The fluid is then examined under a microscope for uric acid crystals, which confirm gout.
• Blood tests – A blood test can measure the levels of uric acid in the blood. Elevated uric acid levels can suggest gout, but this alone is not conclusive, as some people with high uric acid levels do not develop gout. For this reason, blood tests are typically used to rule out other conditions rather than to make a definitive diagnosis.
• Imaging tests – Ultrasound imaging and dual-energy CT (DECT) scans can be used to identify the presence of uric acid crystals in the joints. In addition, X-rays may also be used to rule out other causes of joint pain.
In combination with a detailed medical history review and physical examination, these diagnostic tools allow healthcare providers to accurately pinpoint the root cause of your symptoms and develop an effective treatment plan.
Managing gout effectively requires a combination of medical treatment and lifestyle adjustments. If you’re experiencing symptoms of gout, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. By adhering to prescribed medications and making informed changes to your diet and lifestyle, you can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of gout attacks, leading to a more comfortable and active life. For more information, contact us or request an appointment online. We are located at 203 Hospital Dr, Suite 300B, Glen Burnie, MD 21061. We serve patients from Glen Burnie MD, Pasadena MD, Jacobsville MD, Ferndale MD, Severn MD, and surrounding areas.
Check Out Our 5 Star Reviews


Additional Services You May Need

Additional Services You May Need
▸ Arthritis Care
▸ Infusion Therapy
▸ Lab Services
▸ Radiology
▸ NCARD NRACE
▸ BioFlex Laser Therapy
▸ Ultrasound Guided Injection
▸ NCARD PRP
▸ NCARD Myers
▸ Rheumatology
▸ Myositis
▸ Osteoporosis
▸ Ulcerative Colitis
▸ Multiple Sclerosis
▸ Saphnelo Infusion
▸ Injection Treatments
▸ Intravenous Immunoglobulin Therapy
▸ Asthma
▸ Crohn’s Disease
▸ Fibromyalgia
▸ Infusion Therapy for Gout
▸ Inflammatory Eye Disease
▸ Inflammatory Skin Disease
▸ Vasculitis
▸ Iron Deficiency
▸ Lupus
▸ Toradol Injections